Introduction
Indian Contract Act was enacted on 25 May 1872 and the word ‘ Contract ‘ has derived from the Latin word ‘Contract’ which means to work on contract. The contract comes into force on 1st September 1872.
It extends to the whole of India except Jammu and Kashmir before 31 October 2019.
Definetion
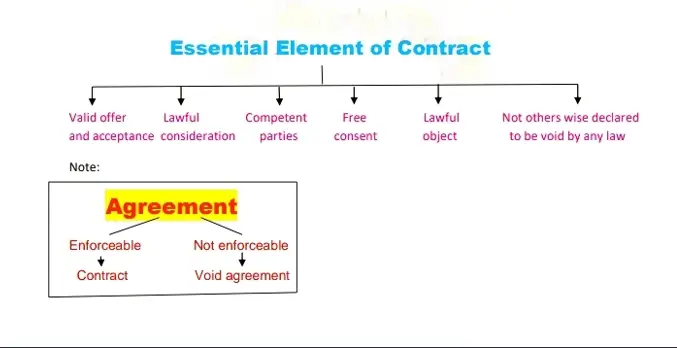
- The term Contract is difines under section 2(h) of Indian Contract Act,1872. section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, of 1872 provides that an agreement enforceable by law is a contract.
- The agreement is difine under section 2(e) of Indian Contract Act,1872. it is provided that every promise and every set of promises forming consideration for each other is an agreement.
- the promise difines under section 2(b) of India Contract Act, 1872. it is provided that a proposal when accepted becomes a promise, thus we can say that a proposal when accepted becomes a promise, and every set of promises is an agreement. Such agreements are enforceable by law, which is called a contract.
- For example, ‘A’ asks ‘B’ if you will buy my car for Rs 5 lac, and ‘B’ replies, ‘ Yes, I will buy your car for 5 lac. This is an acceptance form ‘B’ and section 2(b) says that a proposal when accepted becomes a promise therefore ‘A’ and ‘B’ between a contract.
Two Parties
To constitute a contract, there must be a valid offer and acceptance. The person who offers or makes an offer is called the offeror (promisor) and the other person/party who accepts the offer is called the acceptor (promisee) therefore in every contract, there must be at least two parties (offeror and acceptor).
https://highlawgroup.in/index.php/2024/04/18/type-of-contract-based-on-the-validity-enforceability/
Lawful Consideration
Lawful consideration: Consideration is one of the most essential elements of a contract. The term consideration is defined under section 2(d) of the Contract Act. Proved that, when at the desire of the promisor, the promise or any other person has done or abstained from doing or does, or abstains from doing, or promises to do or to refrain from doing. Something, such act or promise is called a consideration.
Note: Consideration can be past, present, or future
Free Consent
Section 13 of the Indian Contract defines consent. It provides that two or more persons are said to consent when they agree upon the same thing in the same sense and at the same time.
Free Consent is defined under section 14.
Consent is said to be free when it is not caused by the law following factors:
1) Coercion {section (15)}
2) Under Influence {section (16)}
3) Fraud {section (17)}
4) Misrepresentation {section (18)}
5) Mistake {section (20,21,22)}
Lawful Object:
Section 23 of the Indian Contract Act of 1872 defines a legal object as an agreement made for some object or purpose. Such an object is formed based on promises made by the parties. These promises are made either for doing or not doing anything.
For example: A promises to maintain B’s child, and B promises to pay A 1000 rupees yearly. Here, is the promise of each party. They are lawful considerations or lawful objects
For example: A, B and C agree on the division among them of gains acquired or to be acquired, by them by fraud. The agreement is void, as its object is unlawful.





Leave a Reply